
One Page For One Corpus
Google has created a search engine that provides an important service to the world-instantly delivering relevant information on virtually any topic.
Providing the search engines with Information Gain SEO strategies is what is going to get you amazing results in the SERPs.
But how can Google make sure the results they return are quality for the searcher?
The “one corpus for one page” rule is closely linked to user intent so check out why the biggest marketers feel search intent is the number one ranking factor.
Is backlinks a reliable source when they can now be gamed so easily?
Does whoever writes the best content on their website, therefore, make them the best in the industry on a given topic?
“Niche research, keyword research, audience research, SERP analysis, competitor analysis. Measure twice, write once!!”
Has Google just stopped reading your content and ranking your website for keywords? But essentially capable of understanding and recognizing how words shape context through their Rankbrain Artificial Intelligence?
Let me explain to you why the ONE PAGE FOR ONE CORPUS is so important to rank higher in the SERPs.
Contents
What is a Text Corpus?
A Text Corpus is the equivalent of “dataset” in a general machine learning task or SERP set in Google Results. But Corpus is the preferred term, as it already existed previous to the machine learning area to refer to a collection of (data) texts.
Google now collect a set of linguistic data (usually contained in a computer database) used for research and teaching their algorithms known as a text corpus.
In linguistics, a text corpus is a large and structured set of texts (nowadays usually electronically stored and processed). In corpus linguistics, they are used to do statistical analysis and hypothesis testing, checking occurrences or validating linguistic rules within a specific language territory.
Why Google Algorithms Get It Right?
I want to quickly point something out here before I go into detail on – one page for one corpus examples.
Google Search Results return incredible answers to searches and the machine learning algorithms can adjust the results easily in July 2024.
So how does Google Algorithms Get It Right delivering relevant information on virtually any topic?
Content and Links
The core algorithm was built on content and backlinks to rank your websites.
The more content you had and the more quality backlinks you received the better your website ranked.
These core ranking factors are still important to try and get your page onto Page One but then what?
User Engagement Metrics Set The SERP
Once your website is placed onto page one in the SERPs then although more content and links can help, then user engagement metrics set the page one results.
What user engagement metrics can fluctuate results:
- Time on Page
- Quantity of Page Views Per Session
- Bounce Rate
- Page Scroll Depth
- Unique Visitors
- Returning Visitors
- Conversion Rate
- Social Shares
All of these user engagement metrics can feedback into Google Algorithms and educate them which pages are giving the best quality results.
Quality Pages Then Create the Corpus
Now Google has ranked the pages based on the core ranking factors of content and links, then tweaked the results based on best user engagement.
So now Google has the best quality results for a given topic.
These results then are part of the corpus as Google know these results are the best quality.
Therefore, they will only rank high in their search engines new webpages which reflect what they have been educated as being quality.
Rankbrain
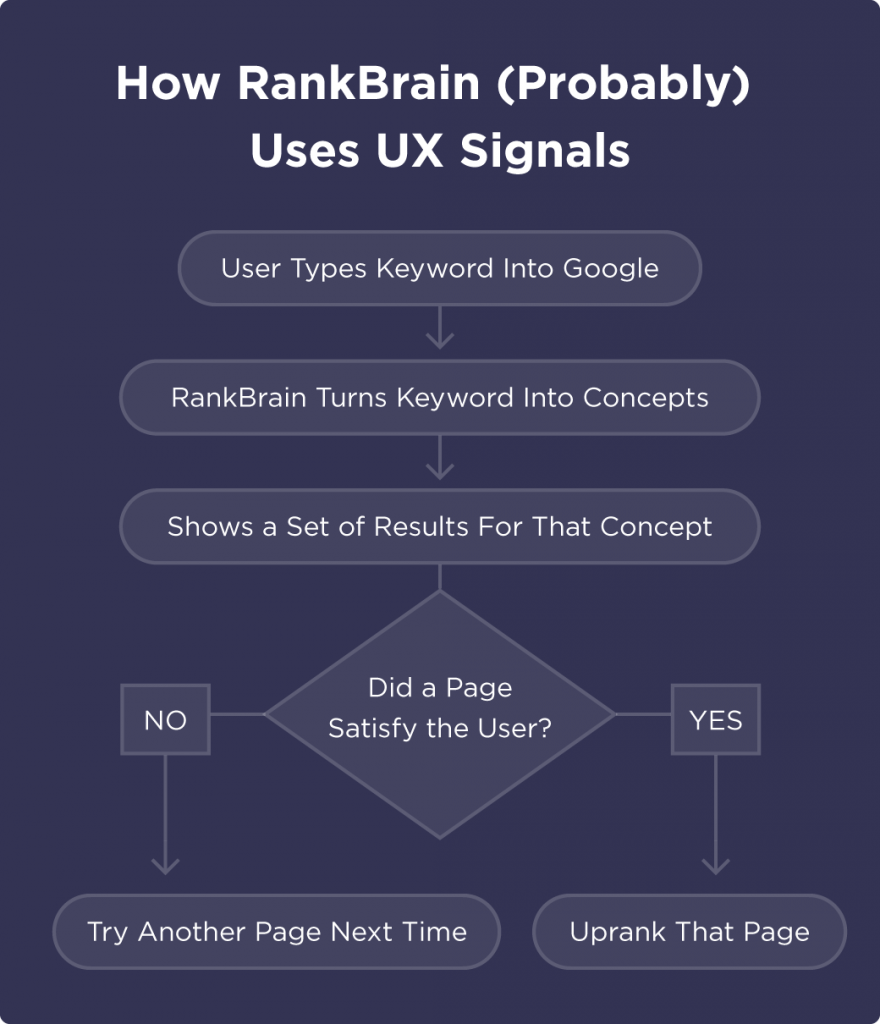
RankBrain is an AI-based system to understand how webpages are related to concepts and topics.
It allows Google to more effectively (and frequently) return relevant webpages even if they don’t contain the exact words used in a search query.
This is achieved by understanding how the page and it’s content is related to other words & concepts.
RankBrain requires a database of relationships, and vectors of known relationships between similar queries, to pull back the best guess.
RankBrain converts the textual contents of search queries into ‘word vectors,’ also known as ‘distributed representations,’ each of which has a unique coordinate address in mathematical space. Vectors close to each other in this space correspond to linguistic similarity
Content, links, and technical SEO are in essence all variables we have a degree of control over – but RankBrain works as an independent algorithm, learning from the datasets we give it (i.e. the content we publish on the internet), so in order to optimise for RankBrain you need to:
- Make sure your content is optimised for high levels of user value through both correct keyword usage and matching the intent
- Make sure your content is structured correctly and presents itself in a meaningful way for users
- Make sure your content is accurate and in correlation with the existing corpus
RankBrain works pretty well and explains datasets and machine learning in a digestible format. Gary Illyes here confirms Rankbrain only deals with the query intent and to better understand parsing of the search queries as still many searches online are unique.
Enter the World of Correlation
As machine learning and rankbrain use their power to understand what the searchers want then if you want to rank on page one you need to reflect the SERPs.
If you do not reflect existing webpages on page one with correlating data you will not rank for your given keyword.
Why? Because over the past decade Google has collated data which tells them the existing first page is what searchers like best.
Google is prioritizing content salience or relevance over trust and authority
SEO Experts in July 2024 are all using tools like surfer SEO to get the correlation data needed to rank higher.
Correlation SEO
It is thanks to SERP Analysis that we are able to discover words that are relevant in terms of the context of a particular expression.
“SERP analysis allows you to optimise the balance of terms in your content according to what is already being shown by the algorithm”
This is perfect for fully optimizing pages, as well as building up relevant topics to garner better SEO results.
It also allows you to rank the words in order from most important to least, which means you can get a clear idea of the scope of the words for the selected topic.
Why One Corpus For One Page?
Now we understand the need for correlating data to rank pages on page one then let me explain the one corpus for one page.
Google creates a set of results for which keyphrase you search and the keywords you want to rank for need to meet the intent of your page.
“Too many SEOs write content and enter into multiple corpuses, which only confuse Google what you actually want the page to rank for”
As Google wants to be sure in returning the best results then they need to be confident your page answers the query perfectly.
Examples To Check
Ok so let’s dive into some interesting data by searching in Google the following and checking the results:
- promo welcome – (you will see this brings back gambling bonus code results)
- promo welcome design – (adding design now changes the corpus to be returning design agencies voucher codes)
- promo welcome boxing – (adding boxing now changes the corpus to be returning boxing betting sites)
- promo welcome fighting – (adding fighting now changes the corpus to be returning MMA fight night passes)
- promo welcome mayweather – (adding mayweather now changes the corpus to be returning Floyd Mayweather promotions company)
The reasons for these examples above is because none of these searches makes much sense but all return results to a corpus where “promo” and “welcome” are used a lot.
But what is alarming is how one word can completely change the intent of the search results.
The same applies to your content and if you enter multiple corpora you are just confusing Google on what you want to rank the page for.
Entering Multiple SERP Corpora
If you start using words that are so rare and unique that only appear in a few documents then maybe you will start drifting apart from the general consensus of that corpus that explains the variance in that keyword SERP set.
One H2 section that falls outside of the intent or topic can completely move your page out of the core corpus group and stop the page ranking (no matter how many links or supporting documents you throw at it)
You need to keep your content within the keyword SERP set and not drift away from the corpus. If you start to move away using rare or unique words to the corpora you want to rank in then this can affect the whole page rankings.
Compete In The Right SERP
There is some SERPs you simply cannot win depending on search intent and choosing the right SERP to go after is the most important part to SEO.
No matter how many links you build or supporting documents you create then if you choose the wrong corpus set and you cannot rank those keyphrases.
To rank high in search, Google must first ensure that the candidate’s content analysis results overcome a saliency threshold before it can turn to other factors — in other words, your content needs to match a number of user search intents.
Improve Your Salience
Raising the salience score to the algorithms on what the page topic is about so they can put you into the correct corpus is key.
The salience score is to do with how confident those words belong in the content corpus.
“Salience shows importance or centrality of an entity to the entire document text, ranges from 0 (less salient) to 1 (highly salient)”
Stacking all the highest salience score keywords to the designated corpus puts you smack bang central to the SERP set of results.
If you do not understand the importance of salience for SEO then make sure to read – What is entity salience and why should SEOs care?
Stacking Key Indicator Words
Stacking your key indicator words and phrases from the text corpus is important to be winning with your onpage.
Here is a video to show how you stack your theme entity central corpus keywords.
After a lot of testing, I have started to understand the importance of stacking the key indicator keywords which are the most central point to the desired corpus you are trying to win in. Some phrases SEOs use for this is:
- Stacking Your Entities
- Stacking Your Central Corpus Keywords
- Stacking Your Highest Value Salience Words
- Stacking Your Most Common Phrases
- The Strongest Salience Scores Need Stacking
N-Grams Is The Key Component
Stacking words on a page is old school and Google have developed further than just word2vec.
Enter the world of N-Grams where the phrases are now more important to any corpus.
The phrases are a sequence of words that occur often in a dataset.
These sequences of words create 2-gram, 3-gram or 4-gram phrases which form a crucial indicator in the corpus set to get into your content.
NLP assign a probability to the occurrence of an N-gram or the probability of a word occurring next in a sequence of words and having these n-grams are the key component to SEO optimised content.
Why N-Grams are the key component:
- It can help in deciding which N-grams can be chunked together to form single entities (like “San Francisco” chunked together as one word, “high school” being chunked as one word)
- It can also help make next-word predictions. Say you have the partial sentence “Please hand over your”. Then it is more likely that the next word is going to be “test” or “assignment” or “paper” than the next word being “school”.
- It can also help to make spelling error corrections. For instance, the sentence “drink cofee” could be corrected to “drink coffee” if you knew that the word “coffee” had a high probability of occurrence after the word “drink” and also the overlap of letters between “cofee” and “coffee” is high.
As you can see, assigning these probabilities has a huge potential in the advancement of Natural Language Processing.
Lucjan Suski
I speak to a lot of high-level marketers and one I have a lot of respect for is Lucjan from SurferSEO and he agreed “100% agree that most common != most important”. The reason for this is because there are so many words which enter into multiple corpora and you need to stack the key indicator keywords that give the confidence the search engines need to know exactly which corpus your webpage is competing in.
“Most common words in a corpus DOES NOT EQUAL TO the Most Important words in that corpus”
Kyle Roof
A great saying by Kyle Roof on a recent podcast with Authority Hackers was:
“The existence of a signal is the #1 ranking factor. It is better to have something in a signal area than nothing. The non existence of a ranking factor is a ranking factor”
This resonated a lot with me because I found by far the biggest jumps were made when I managed to find these missing key indicator keywords and added them just once on the page. I tried adding a second or third time with little gains. But the jump from, not having it on the page, to having it just once, made huge jumps in rankings.
“The key indicator words are important keywords needed on the page that are rarely used elsewhere on other documents – so search engines can distinguish very quickly the corpus of the given page when these important keywords are used”
While adding these key indicator keywords to your page hugely helps your rankings, in contrast, adding words from outside your corpus can confuse the search engines and cause your whole page to not rank on page one for this very reason.
If we rank position one for the phrase stacking then this could improve our correlation score to rank the primary keyword.
Related Reads
Here is a collection of related articles that are worth understanding:
- Your Best Word Vector Tool For Content Gap Analysis
- Google Brain Word Vectors Approach
- Semantic For Google Search
- Using word vectors and applying them in SEO
- Word Vector SEO Guide
- Keyword Extraction
- Mine the SERPs for SEO
- Strategies using Natural Language Processing
These are some great guides to educate on making sure you understand the correlation, word vectors, corpus SEO and SERP analysis.
Conclusion
Make sure to analyze SERPs for your keywords before optimizing your page to rank for them.
But remember one page needs to stay within one corpus.
“Do SERP analysis for every keyword you plan to optimize for. SERP analysis checks the search intent and corpus in which the keyword fits into”
If you start to add h2s to the page outside of the designated corpus this will stop all your keywords from ranking as will skew the data.
- Absolute Links vs Relative Links

- AI Content Detection
- AI Copywriting Software

- Artificial Intelligence For Content Writing

- Autoblogging AI Review

- Bolded Keywords in Google SERP
- Content Briefs

- Content Cannibalisation Google Penalty

- Content Decay

- Content Doctor

- Content Expansion

- Content Harmony Review

- Content Plan Roadmap
- Content Strategist

- Content Team

- Dashword Review

- Featured Snippets
- Focus Keyphrase

- Google Duplicate Content Penalty

- Google Fresh Content Ranking Factor

- How To Create A Topical Map

- Identify The Root, Rare, and Unique Attributes Of An Entity

- Jasper.ai Free Trial

- Onboarding Writers

- One Page For One Corpus

- Ordering Content SOP

- Page Optimizer Pro

- Page ReWriter Review
- Passage Ranking

- Progressive Content Optimisation SEO

- Search Perspective Frameworks

- SEO Avalanche Technique
- SEO Content Audit Guide

- SEO Content Optimization Tools

- SEO Content Writers

- Silo Internal Linking

- Standalone Content

- Stealth AI Writer

- Surfer AI Writer

- Surfer SEO Review

- Text Optimizer

- Text Structure

- The SEO Power of Concise Writing

- Topical SEO - Create Supporting Articles

- Use Topic Review
- Website Content Uploader

- Why Is Content Veggie The Best AI Content Tool for SEO?
- Workello


About FatRank
Our aim to explain and educate from a basic level to an advanced on SEO and Social Media Marketing.
